HL Plant Biology - Activities for Learning
Lesson Plans for the HL Plants Topic
The ideas for learning activities on this page aim to cover the whole of the IB guide for this topic. Where a full lesson plan has been developed it includes resources to use on an interactive whiteboard and worksheets to print. There is a mix of laboratory work, theory lessons, and assessment materials with model answers.
Transport in xylem - planning 9.1This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. It could be useful for planning | |
 | Leaf stomata & transpiration (the guard cell's dilemma)A short video introduction to the roles of cells in a leaf followed by some simple note taking about leaf structure and function. The function of stomata is linked to carbon dioxide absorption and also to the problem of water loss. Finally, some simple questions test knowledge at the end. |
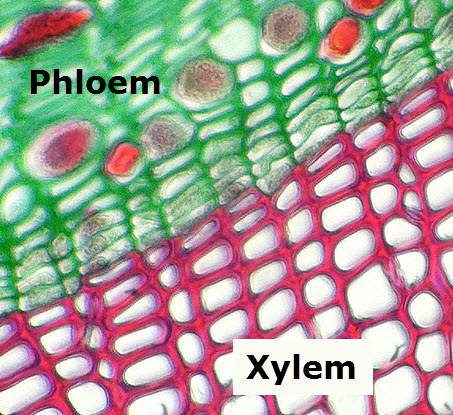 | Vascular tissues - introductionTime: 1hr This lesson begins with a hands-on look inside the roots and stems of plants to see that the cells are not all the same and that there are specialised cells helping the plant to transport water and sugars. Not to mention supporting the plant. A short research task is designed to help students find the key details about xylem and phloem which will be needed in the following lessons. Finally, some simple questions tests factual recall. |
 | Transport in xylemTime 1h: This lesson follows on from the lesson on vascular tissues and explores the details of the way water travels through plants and how the plant is adapted to facilitate this transpiration stream. The movement of mineral ions and the role of mutualistic fungi a Experiments on Transpiration (new guide) Transpiration and Xerophytes (new guide) re also included. The role of water and vascular tissue in the support of plants includes the presence of thickened cellulose, cell turgor and lignified xylem. The role of phloem in translocation of sugars makes a good comparison activity. |
 | Transpiration and XerophytesTime:1hr This lesson builds on the adaptations of the plant to enable transpiration covered in lesson 4. The difference between transpiration and transpiration stream is clarified and the factors which control transpiration rates are explored, including; opening and closing of guard cells, the plant hormone abscisic acid and abioic factors. Once this is understood students can apply their understanding to adaptations of xerophytes. |
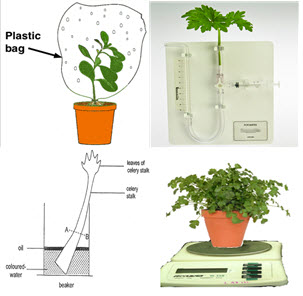 | Experiments on TranspirationTime: 1h Using potometers is a nice way to explore the relationship between abiotic factors and transpiration rates. This experiment could be adapted and used as an investigation. Much depends on the equipment available and there are some suggestions for simple versions of these experiments in this lab. |
 | Transpiration and XerophytesThis lesson builds on the adaptations of the plant to enable transpiration. The abiotic factors which affect transpiration rates are introduced and students are asked to explain how each adaptation affects transpiration. Once this is understood students apply their understanding to adaptations of xerophytes in some IB style questions.Why is a good day for drying your washing a difficult day for plants? |
Transport in phloem - planning sheet 9.2A short activity introducing phloem sieve tubes and translocation using a video and a worksheet followed by a data processing question including the identification of phloem in slides and the use of aphid stylets in translocation experiments. | |
 | Phloem and translocationA short activity introducing phloem sieve tubes and translocation using a video and a worksheet followed by a worksheet outlining some experiments to measure translocation direction and rates and some data analysis questions. A quiz includes the identification of phloem in slides of stem and root tissues. |
Growth in plants - planning sheet 9.3This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. It could be useful for planning | |
 | Meristems and GrowthTime: 1h What is a meristem and how is it that a plant can keep growing for the whole of its life? Micropropagation using the plant meristems as a source of undifferentiated cells has become an important method of producing plants for agriculture and for conservation. This short lesson is in the style of a web-quest and uses a student worksheet to help students structure their notes. |
 | Hormonal control in plantsTime: 1h How do plants respond to light if they don't have eyes nor a brain? The mechanism is quite complex but it is a good illustration of the role of membrane proteins and the fluid nature of the plasma membrane. There are two activities in this lesson, the first is a set of slides with some questions and the second is a very short video clip followed by some more questions. There are model answers provided for both sets of questions. |
Reproduction in plants - planning sheet 9.4This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. It could be useful for planning | |
 | Reproduction in angiospermsTime: 2h The structure of animal-pollinated flowers is very varied and lends itself to a nice 'dissection' in this experiment. Comparisons of different flowers help students to understand the functions of each part. The dissection of a seed complements this nicely especially if the seeds have been germinating for a couple of days first. |
 | Seeds, flowering & phytochromesSeeds are a crucial part of plant reproduction and there are many methods used by plants for seed dispersal. This activity covers both seed structure and dispersal. Flowering in any plants takes place at specific times of the year. The timing of flowering is controlled by phytochromes (Pr & Pfr) which enable plants to detect day length and control gene expression. A set of slides helps to explain this process. |
IA planning skills lesson - seed germination experimentThis is going to be a simple activity to plan an experiment. |

